IoT Firewall Guide: Secure Your Devices & Network - Now!
Are you concerned about the security of your smart home or business network? In today's interconnected world, securing your Internet of Things (IoT) devices is more critical than ever, demanding a proactive and informed approach to cybersecurity.
The proliferation of IoT devices, from smart thermostats and security cameras to industrial sensors, has created a vast attack surface for cybercriminals. These devices, often designed with minimal security features, are vulnerable to exploitation, potentially leading to data breaches, privacy violations, and disruption of critical services. Protecting these devices requires a layered approach, with IoT firewalls playing a crucial role.
Here's a look at how to protect yourself.
Understanding IoT Firewalls
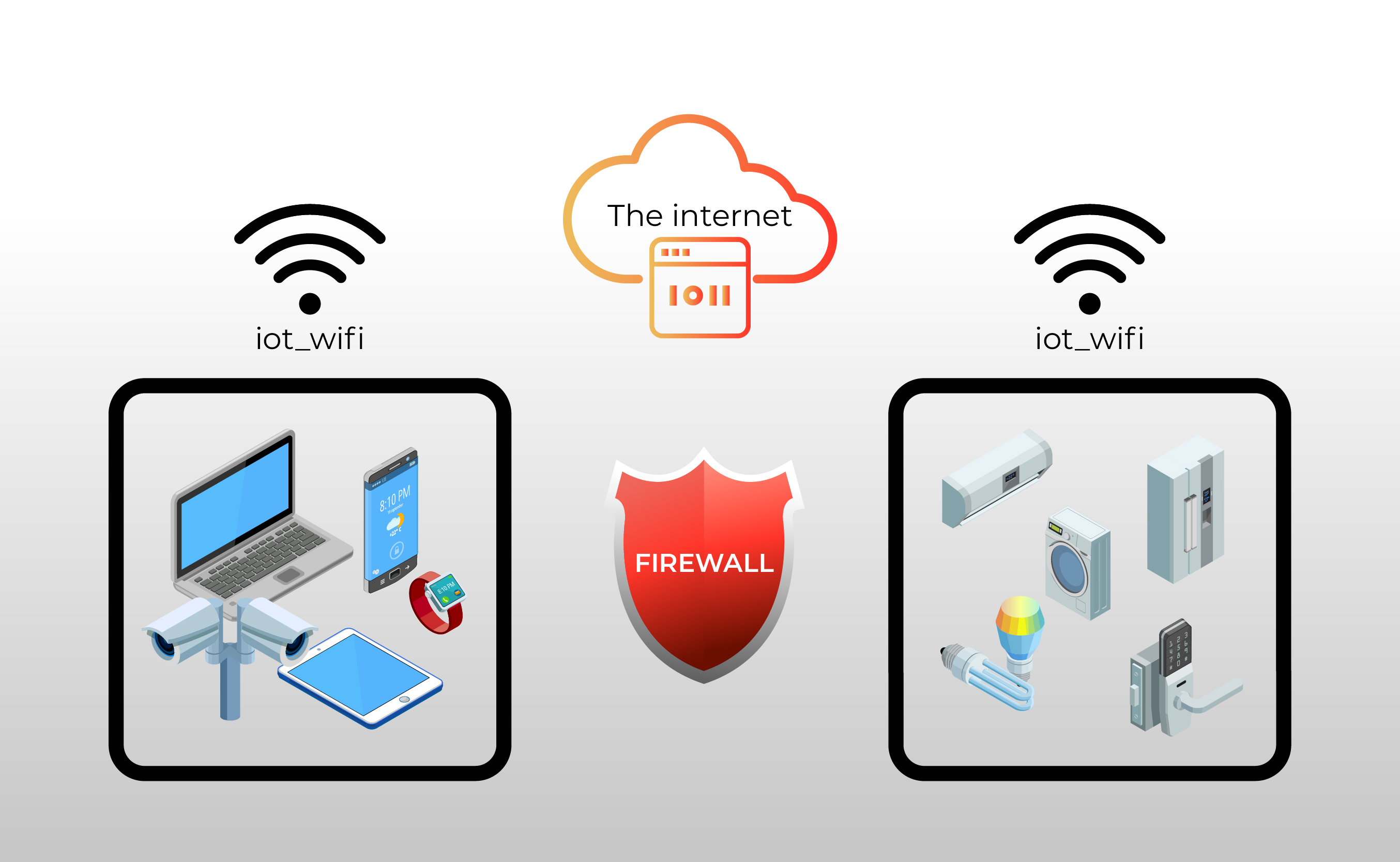
The concept of an IoT firewall is central to modern network security. As the number of "things" connected to the internet continues to explode, so too does the need for specialized security measures. These innovative solutions go beyond traditional firewalls, blending their strengths with meticulous application monitoring. This combination provides comprehensive support for a diverse range of IoT devices and protocols. This is particularly relevant in a smart home setting, where an IoT firewall acts as a vigilant guardian, watching devices like thermostats and cameras for unusual behavior that could signal a security problem.
IoT firewalls control data flow inside an internet of things system in addition to monitoring data flow. To regulate communication between the aforementioned devices and external networks, they employ encryption, traffic filtering, and access control rules. Internet of things firewalls analyze data traffic from connected devices to find security risks, unusual patterns, or unauthorized access attempts.
The evolution of IoT security has been marked by challenges, including the need for specialized security solutions tailored to the unique limitations of IoT devices. These devices, often with limited resources and long lifespans, require security measures that are both effective and efficient.
Key Components of an IoT Firewall Strategy
Several elements are important for a successful IoT firewall strategy.
- Identification and Classification of Devices: A foundational step involves meticulously identifying and classifying all IoT devices on your network. This can be achieved through various methods, including network scanning, device fingerprinting, and analyzing network traffic. Accurate device identification enables you to apply specific security policies tailored to each device type.
- 24x7 Risk Monitoring: Comprehensive monitoring is critical. This involves continuously analyzing device behavior, assessing their security posture, and generating alerts for potential vulnerabilities. This real-time monitoring should be integrated with a constantly updated Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) inventory to quickly identify and address known threats.
- Application-Level Inspection: Unlike traditional firewalls that primarily focus on network and transport layers, IoT firewalls must inspect traffic at the application layer. This allows for a deeper understanding of the data being exchanged, enabling the detection of malicious payloads or suspicious activities within the application data.
- Micro-Segmentation: Micro-segmentation involves dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments. This limits the impact of a security breach by restricting lateral movement within the network. In the context of IoT, this can mean isolating different types of devices from each other, preventing a compromised camera from accessing sensitive data on your network.
- Zero Trust Principles: Implement zero-trust security policies, which assume that no user or device can be trusted by default, whether inside or outside the network perimeter. This requires strict authentication and authorization for all devices and users, along with continuous monitoring and verification of their activities.
The convergence of these elements forms the basis of a robust IoT firewall strategy, creating a secure and resilient network infrastructure.
Types of Firewalls for IoT Devices
The diversity of internet of things devices entails the emergence of several types of firewalls, each with its own features and advantages, as well as differences in functionality, architecture, detection techniques and prevention of attacks from cybercriminals. Here's an overview of different types:
- Network-Based Firewalls: These are the most common type, typically hardware or software appliances that sit at the edge of your network. They filter traffic based on IP addresses, ports, and protocols.
- Application-Layer Firewalls: These firewalls inspect traffic at the application layer, which is useful for identifying and blocking malicious activity.
- Host-Based Firewalls: These firewalls run on individual IoT devices and monitor traffic to and from that specific device.
- Cloud-Based Firewalls: These are cloud-hosted firewalls that provide protection for IoT devices that are connected to the cloud.
Setting up Firewall Rules
Implementing effective firewall rules is paramount to securing your IoT network. Here are some key steps to take:
- Define Security Policies: Begin by establishing clear security policies that outline the allowed and disallowed network traffic for your IoT devices. Determine which devices need to communicate with the internet and which should only communicate within your local network.
- Identify IoT Devices: The first step in securing your IoT network involves a thorough identification and classification of all devices. This includes noting the device type, manufacturer, model, and the specific functions it performs. This is one of the preparations before implementing an IoT firewall. Iot security provides the firewall with a device dictionary file containing a list of device attributes such as profiles, categories, vendors, and models.
- Create a Device Dictionary: Consider creating a device dictionary file that contains information on the device's attributes such as profiles, categories, vendors, and models. This file allows the firewall to recognize specific devices and enforce policies effectively.
- Implement Segmentation: Utilize VLANs (Virtual LANs) to segment your network, isolating IoT devices from your main network. This limits the impact of a potential breach. Create two new VLANs: one for all of your IoT devices. This ensures that these devices are isolated and cannot directly communicate with other devices on your network unless specifically allowed by firewall rules.
- Establish Access Control Rules: Create explicit firewall rules to control traffic flow between different VLANs. These rules should specify which devices or services are allowed to communicate and the direction of the traffic.
- Restrict Internet Access: Limit outbound internet access for your IoT devices, allowing only necessary connections. This prevents devices from communicating with potentially malicious servers.
- Regularly Review and Update: Constantly review and update your firewall rules. As new IoT devices are added to your network, adjust your rules to maintain the right balance between security and functionality.
Accessing Devices Behind a Firewall
Here are key steps for accessing devices behind a firewall:
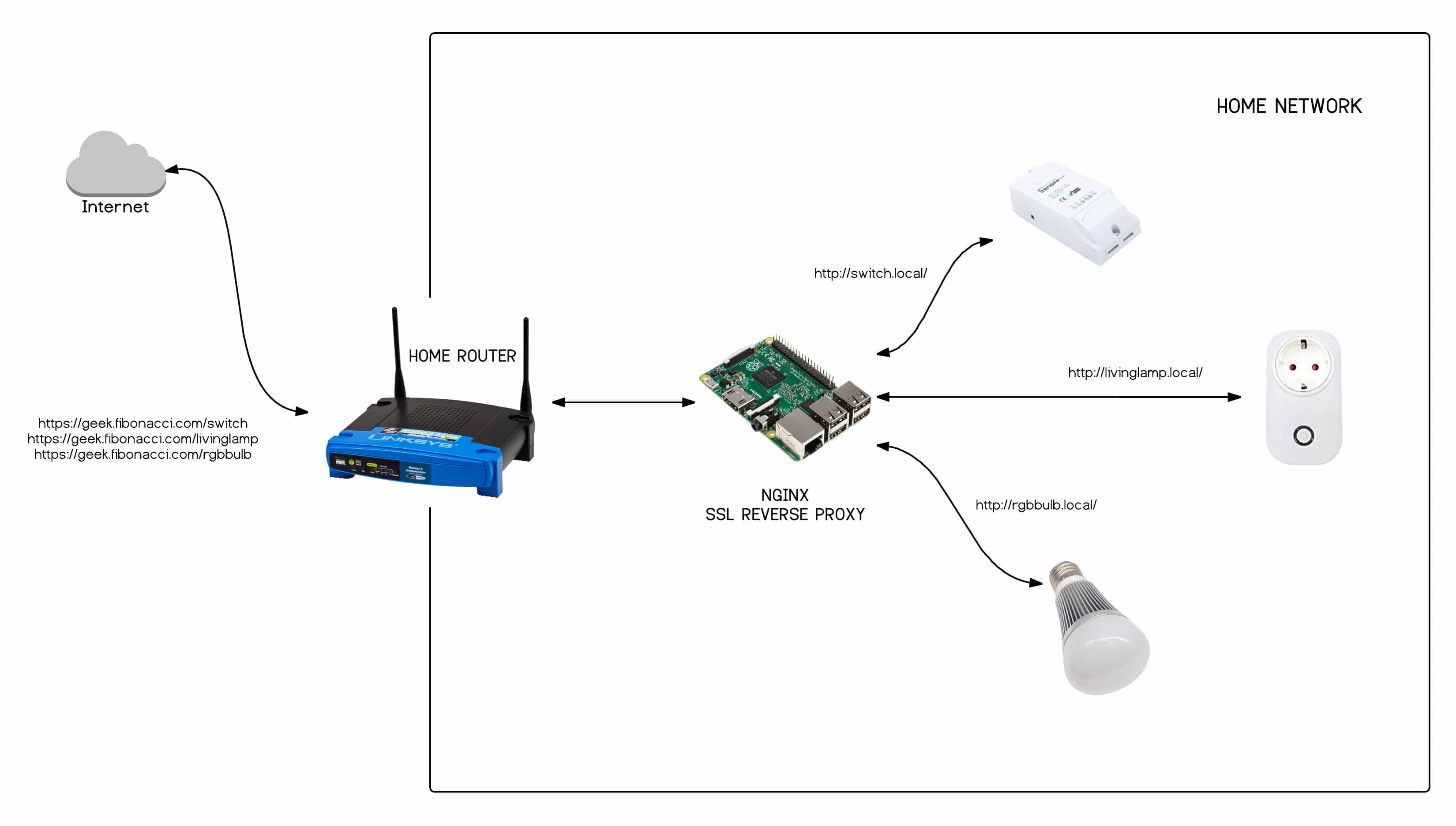
- Port Forwarding: Configure port forwarding on your firewall to allow access to specific services or applications running on your IoT devices. This is often necessary when you want to access these devices from outside your local network.
- VPN Access: Set up a Virtual Private Network (VPN) server on your network. This allows you to securely connect to your home network from anywhere in the world and access your IoT devices as if you were on your local network.
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone): A DMZ is a network segment that is isolated from both your internal network and the public internet. You can place an IoT device in a DMZ if you need to make it accessible from the internet. However, this should be approached with caution due to the increased security risk.
- Whitelist IP Addresses: If you need to access devices behind the firewall from specific IP addresses, create a whitelist. This involves creating firewall rules to allow traffic from these specific IP addresses.
These methods allow you to access your devices securely while still maintaining the protection provided by the firewall.
Securing Your Network
To enhance the security of your network, consider the following additional measures:
- Regular Updates: Keep the firmware and software of your IoT devices and your firewall up to date. Manufacturers release updates to address security vulnerabilities and improve performance.
- Strong Passwords: Change the default passwords on your IoT devices and choose strong, unique passwords. Avoid using easily guessable passwords.
- Network Monitoring: Implement network monitoring tools to detect and alert you to suspicious activity or unusual patterns.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Regularly scan your network for vulnerabilities to identify potential weaknesses.
- Guest Network: Use a guest network to isolate untrusted devices from your main network, adding an extra layer of security.
- Review Logs: Regularly review your firewall logs to monitor traffic, detect potential security incidents, and identify suspicious activity.
Practical Applications
In a smart home environment, an IoT firewall is invaluable.
- Thermostats and Cameras: The firewall can monitor devices like smart thermostats and security cameras, spotting unusual behavior that could signal a security problem.
- Home Assistant Integration: To address your Home Assistant requirements, configure your firewall settings to allow the Home Assistant instance to communicate with the IoT devices on your dedicated IoT network (VLAN).
- Isolation: Implement network segmentation, such as through VLANs. This will involve creating a dedicated VLAN for your IoT devices, such as Wyze cameras or Nest thermostats. This isolation ensures that even if a device is compromised, the attacker's lateral movement is limited.
- Firewall Rules: Within the firewall, you'll need to create rules to control traffic flow between your main network, the IoT VLAN, and the internet.
Sophos Home and IoT Security
It's important to note that Sophos Home, a security product designed to protect computers, has certain limitations in the context of IoT security. Sophos Home won't control IoT devices. Sophos Home won't control IoT devices, but end points with Sophos Home will be protected from IoT devices. Sophos is a cheap alternative if you just want to protect computers from iot, rogue devices, zombie devices, and other issues.
Ubiquiti Dream Machine Pro and IoT Firewall
For those using a Ubiquiti Dream Machine Pro (UDM-Pro), integrating VLANs and firewall rules is a common approach to segmenting and securing IoT devices. While Ubiquiti provides a user-friendly interface for managing these settings, understanding the underlying principles is crucial for optimal configuration.
In a Ubiquiti setup, the process would involve:
- VLAN Creation: Creating a new VLAN for IoT devices.
- Firewall Rule Configuration: Establishing firewall rules to control traffic between different VLANs.
- Layer 3 Switch Considerations: For making IoT devices controllable from the main SSID, a layer 3 switch might be required.
Troubleshooting and Advanced Configuration
To effectively secure your IoT network, consider the following troubleshooting techniques:
- Network Segmentation: The idea is to create separate VLANs for your IoT devices.
- Firewall Rules Configuration: After creating your IoT VLAN, configure firewall rules to control the traffic flow.
- Home Assistant Accessibility: Create specific rules to allow communication between Home Assistant and your IoT devices.
- Device Isolation: The fundamental idea is to isolate your IoT devices from the rest of your network.
Challenges in Building Security into IoT Devices
Challenges in building security into IoT devices include:
- Specialized Nature: IoT devices are specialized, and there is no "one size fits all" security solution for them.
- Limited Resources: Many IoT devices have limited resources, such as processing power and memory, which limits the complexity of the security features that can be implemented.
- Long Lifetimes: IoT devices often have lifetimes measured in decades, which means that they must be secure for a long time.
Best Practices
Here are some best practices for securing your connected devices:
- Identify Devices: Begin by identifying all IoT devices and their functions within your network. This will help you create customized security policies.
- Segment Your Network: Use VLANs to segment your network, separating IoT devices from more sensitive devices and traffic.
- Apply Zero Trust: Implement zero-trust security principles.
- Update Regularly: Ensure you keep your IoT devices' firmware and your firewall software up-to-date to patch vulnerabilities.
- Monitor Constantly: Use network monitoring tools to detect and respond to suspicious activity.