IoT Firewall Guide: Secure Your Devices & Network!
Are you concerned about the security of your smart home, connected devices, and the ever-expanding Internet of Things (IoT)? Protecting your network from cyber attacks is no longer optionalit's essential in today's connected world, and understanding the role of IoT firewalls is the first step.
The digital landscape has undergone a dramatic transformation, with the proliferation of interconnected devices reshaping how we live, work, and interact with the world around us. From smart thermostats and security cameras to voice assistants and wearable gadgets, the IoT has woven itself into the fabric of modern life. While these devices offer convenience and enhanced functionality, they also introduce new vulnerabilities and security challenges that must be addressed to safeguard our digital lives.
Internet of Things (IoT) firewalls are becoming increasingly important tools in the quest to protect our networks from these evolving threats. These specialized firewalls are designed to analyze data traffic from connected devices, identifying security risks, unusual patterns, and unauthorized access attempts. Their role goes beyond simple monitoring; they actively control data flow, employing encryption, traffic filtering, and access control rules to regulate communication between devices and external networks. In essence, IoT firewalls act as vigilant sentinels, monitoring and managing the flow of information within an IoT ecosystem.
Consider the following table, presenting key insights into the functionality of an IoT firewall:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Traffic Analysis | Monitors data traffic to detect security risks, unusual patterns, and unauthorized access attempts. |
| Data Flow Control | Regulates communication between devices and external networks. |
| Encryption | Employs encryption to protect data transmitted over networks. |
| Traffic Filtering | Filters network traffic based on predefined rules to block or allow specific types of data. |
| Access Control | Implements access control rules to manage which devices and users can access specific resources. |
The architecture of an IoT firewall is typically designed to be adaptable and effective, capable of managing the specific challenges posed by IoT devices. These devices often have limited resources and specialized functions, requiring a firewall that can be tailored to their needs. Embedded firewalls, for example, are designed to work on these resource-constrained devices, ensuring that security measures do not unduly impact performance.
Several types of firewalls cater to the diverse landscape of IoT devices. Each offers unique features and advantages, depending on their architecture, detection techniques, and attack prevention mechanisms. Understanding these types is critical to selecting the right security solution.
One crucial aspect of securing IoT devices lies in identifying and classifying them. This involves creating an inventory of all connected devices, a critical step before implementing any firewall. Once identified, devices can be categorized, and their network behavior analyzed. Machine learning can play a significant role here, enabling the firewall to learn the normal behavior of each device and flag any deviations that might indicate a security breach.
The practical implementation of an IoT firewall involves several steps. First, the network administrator must configure the firewall to collect network traffic metadata and forward it to a logging service. This is essential for monitoring and analysis. A device certificate should also be installed, adding an extra layer of security. The firewall rules must be carefully designed to regulate traffic flow, blocking unauthorized access and allowing legitimate communication. Tools like the dictionary file, which provides a list of device attributes, can be used for selecting recommended security policy rules and creating custom rules. Finally, ongoing monitoring and updates are essential to adapt to the ever-changing threat landscape.
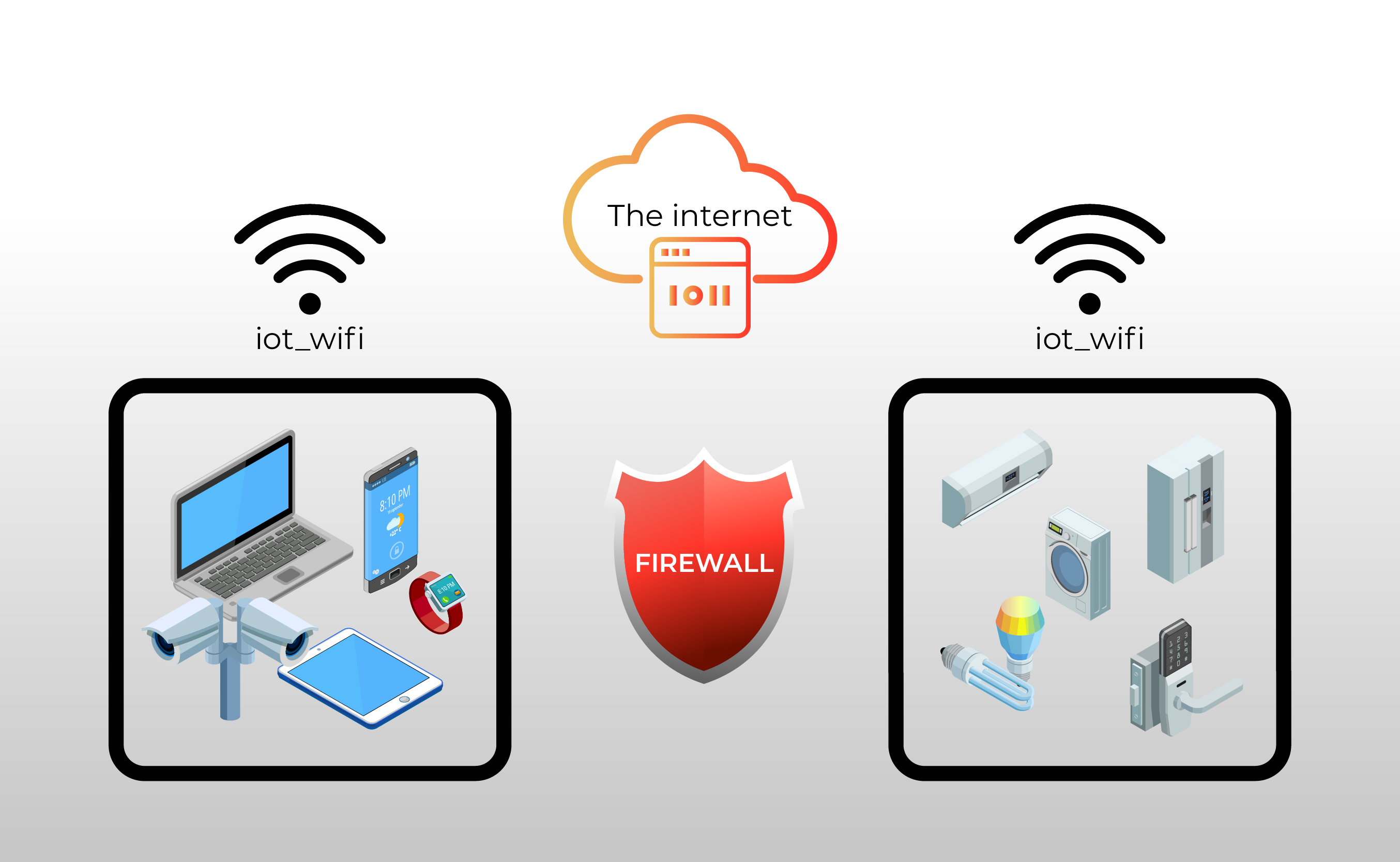
Consider a smart home environment. An IoT firewall will monitor devices like thermostats and cameras, looking for unusual behavior that might signal a security problem. If a camera suddenly starts sending data to an unfamiliar server or a thermostat begins communicating with unauthorized entities, the firewall can flag the activity and alert the homeowner. In addition, IoT devices often require access to the internet, but it is often beneficial to control which calls these devices are allowed to make, thus limiting potential points of compromise. By employing VLANs and carefully designed firewall rules, you can segment your network and control communication, providing better security and network management.
The process of securing IoT devices often involves hardening them through IoT endpoint protection, which complements firewall protection. This includes identifying all devices, classifying them, and continuously monitoring them for risks. 24/7 risk monitoring and the use of a CVE (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) inventory provide another layer of security.
For those setting up IoT networks, it is important to understand how to configure devices to work effectively behind a firewall. This includes understanding the need to allow specific types of traffic for devices like those in a smart home. Devices may require access to smartphones or other devices on your LAN. In these cases, tools such as Avahi (easily setup on pfSense) can be used. This approach allows the LAN to access the IoT devices while preventing the IoT devices from accessing the LAN.
One popular approach involves the use of VLANs (Virtual LANs) to segment your network. By creating separate VLANs for different types of devices, you can isolate them from each other and limit the potential impact of a security breach. When creating a VLAN, a careful review of existing security policies and consideration of existing network architecture is critical. An example would be creating two new VLANs: one for the IoT devices and another for the normal LAN.
In terms of device-specific configuration, consider a network with a Dream Machine Pro, a 16-port PoE switch, and multiple access points. To control IoT devices from the main SSID, a layer 3 switch might be required. This provides the necessary functionality to route traffic between VLANs. Similarly, for services such as Home Assistant, the network setup must allow for interoperability. The goal is to isolate the IoT devices while still allowing them to communicate with services that they need to function.
When configuring your firewall, remember that there is no one size fits all security solution for IoT devices. Instead, it is essential to tailor the approach to the specific devices and their traffic patterns. This will include setting up the firewall rules to restrict traffic to only authorized destinations.
Embedded firewalls are designed to work on specialized, resource-constrained devices and should be portable, scalable, easily managed, and tailored to support IoT use cases. These firewalls often have advanced features, such as the ability to block any traffic addressed to unauthorized destinations, as well as raising an alert when a device is behaving abnormally. This is made possible by using machine learning to understand the usual traffic patterns and using this knowledge to detect irregularities.
Before deploying an IoT firewall, a key preparation is identifying all used IoT devices. Identifying and understanding the device attributes allows you to make informed decisions on security policy rules. In addition, you can configure your firewall to give new, unidentified devices default network access so they can establish their normal behavior. After the baseline behavior is established, the firewall can apply policy rules to traffic to and from those new devices based on a device id attribute.
There are multiple challenges building security into IoT devices, including their specialized nature, limited resources, and often long lifespans. IoT device developers need specialized security solutions designed specifically for their needs. Furthermore, when deploying an IoT firewall, youll want to configure it to analyze data traffic and look for security risks. Then, configure your firewall to collect network traffic metadata, forward it to the logging service, and install a device certificate.
To further illustrate the concept, consider this table with general information about the different types of firewalls for IoT devices:
| Type of Firewall | Description |
|---|---|
| Embedded Firewall | Designed for specialized devices with limited resources, must be portable, scalable, and easily managed. |
| Network Firewall | Traditional firewalls adapted for IoT environments, typically placed at network entry points. |
| Application-Layer Firewall | Inspects application-layer traffic, providing deep packet inspection and application-aware security. |
| Cloud-Based Firewall | Operates in the cloud, providing security services for devices connected to the internet. |
Securing the IoT involves multiple steps, from identifying devices and classifying them to establishing a baseline of normal behavior and applying firewall policies. It's crucial to address the fact that IoT devices often have predictable traffic patterns, enabling firewalls to block unauthorized traffic and alert administrators to anomalies. Remember, IoT security also uses machine learning to identify vulnerabilities and assess risk in devices based on their network behavior.
In closing, the rapidly evolving landscape of the Internet of Things presents both exciting opportunities and significant security challenges. By understanding the critical role of IoT firewalls, you can proactively protect your network from cyber attacks and secure your connected devices against emerging threats. Remember to learn about the different types of firewalls, how to set up rules, and how to access devices behind a firewall to fortify your digital defenses.